Zero Trust Security is an approach to cybersecurity that challenges the traditional notion of trust within a network. It operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” In a Zero Trust model, no user or device earns automatic trust, regardless of location, inside or outside the network perimeter.
Why You Should Adopt Zero Trust Security
As cyber threats evolve, traditional security measures are losing their effectiveness. The rise of cloud services, mobile devices, and remote work has made the traditional network perimeter porous. Enter Zero Trust Security: a solution that tightens access controls and monitoring at every level of your network, reducing vulnerabilities and making it harder for attackers to move around undetected. Here's why adopting Zero Trust Security is crucial for your business.
Zero Trust Security operates on several key principles that collectively create a robust cybersecurity framework:
Principle 1: Verify Every User and Device
Gone are the days of blind trust based solely on network location. Every user and device must undergo rigorous verification before accessing your network. This means employing strong authentication methods like biometrics and multi-factor authentication.
Principle 2: Least Privilege Access
Grant users and devices access only to what they need to perform their roles. This helps contain potential breaches by restricting lateral movement within your network.
Principle 3: Assume Breach
Adopt a proactive mindset that assumes breaches are either happening or imminent. Develop robust incident response strategies to swiftly detect, contain, and mitigate threats.
Principle 4: Microsegmentation
Segment your network into smaller zones with specific security controls. This limits the impact of breaches and minimizes the attack surface.
Principle 5: Continuous Monitoring
Constantly monitor network traffic, user behavior, and system anomalies to detect and respond to threats in real time.
Principle 6: Assume Everything is Vulnerable
Rather than fearing vulnerabilities, anticipate them and implement strategies to mitigate risks. This includes regular patching, penetration testing, and secure coding practices.
Principle 7: Apply Security Controls Adaptively
Adjust your security measures based on real-time threat assessments. Utilize predictive analytics and dynamic access controls to stay ahead of evolving threats.
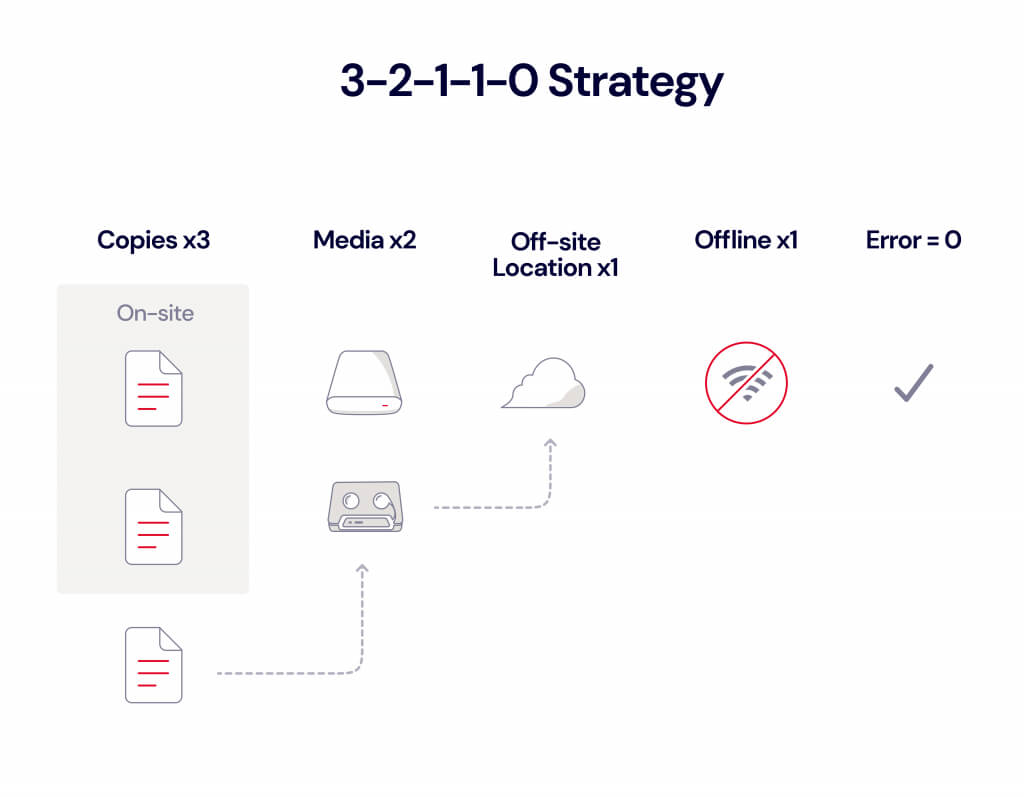
Principle 8: Comprehensive Backup and Recovery
Implement robust backup and recovery procedures to ensure the resilience of your data and systems. Regularly back up critical data and configurations, storing them securely offsite or in a separate network segment. Test your backup and recovery processes regularly to ensure they are effective in restoring operations in the event of a breach or system failure.
To successfully implement Zero Trust Security, follow these steps:
Assess Your Current Security Posture
Conduct a thorough security audit to identify vulnerabilities and entry points for attackers.
Design a Zero Trust Security Framework
Plan and map out network segments, access controls, and monitoring strategies. Invest in the right security technologies to bolster your defenses.
Establish Policies and Procedures
Keep a close eye on network activities and respond swiftly to emerging threats. Adapt your security controls as needed to stay ahead of attackers.
In an era where digital evolution often equates to vulnerability, the adoption of Zero Trust Security transitions from a luxury to an imperative. These seven principles combine to erect an unassailable digital stronghold, defending against a myriad of cyber threats. The imperative is clear: elevate cybersecurity as a priority, advocate for Zero Trust Security, and foster a vigilant culture. In doing so, you erect barriers against the ceaseless onslaught of cyber threats.