As you all should know, nowadays phishing is a technique for attempting to acquire sensitive data, such as bank account numbers, crypto wallet details through a fraudulent solicitation in email or on a web site, in which the perpetrator masquerades as a legitimate business or reputable person.
In this article we will present 5 phishing techniques that you should be aware of it.
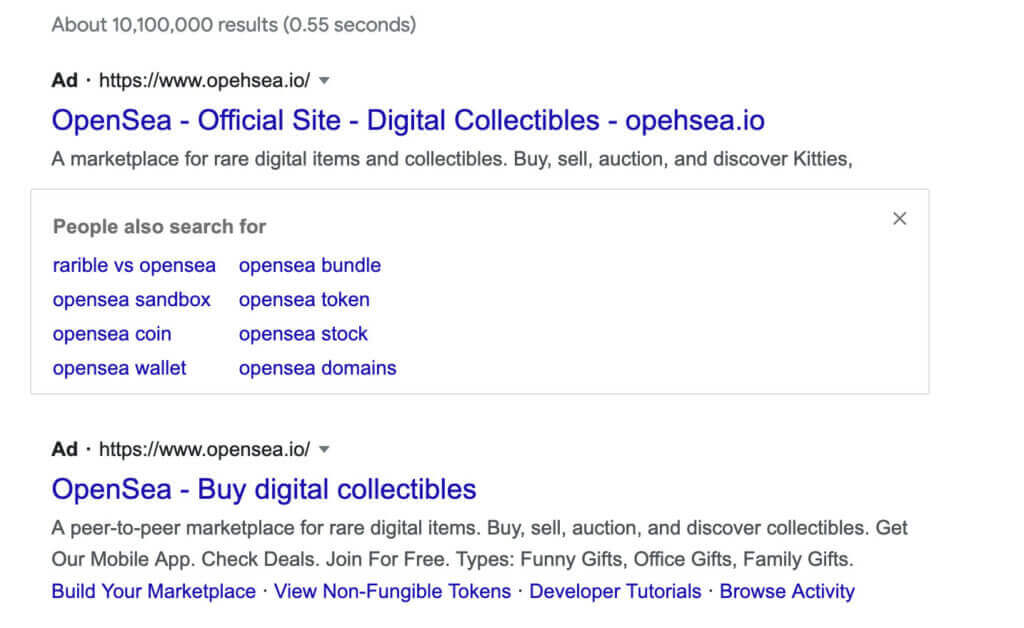
Attackers are trying to improve their tactics, so we may often see look-alike domains. Here are couple of examples that we spotted lately:
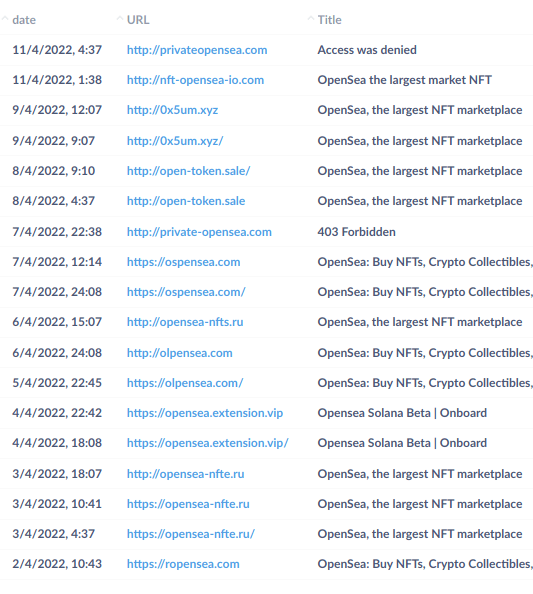
We wrote an explanation of how experienced crypto investor lost $1.7M in hot wallet hack. From that example it is obvious how important is to understand e-mail headers and not to fall into the trap of scammers.
Here is an example of phishing e-mail that we generated in order to explain some details from email header. This is a classic e-mail spoofing attack:
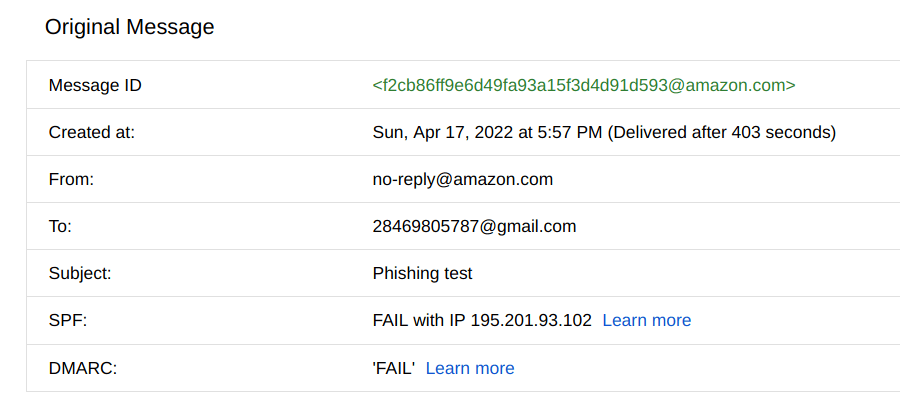
So, as you may see we have sent an e-mail pretending to be "no-reply@amazon.com" by using our mail server. If you are using Gmail then by clicking on "show original", Google will reveal some of the details, including mail security protocols.
Before we continue we need to explain what are those protocols SPF, DMARC and DKIM.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are the three main email security protocols that complement one another. Put simply, they are methods to authenticate a mail server and help prove to Internet Service Providers (ISPs), mail services, and other mail servers that senders are truly authorized to send an email.
SPF: Sender Policy Framework
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) works by strictly determining the number of allowed IP addresses that can send emails from your domain. Or in other words it is a DNS record containing information about servers allowed to send emails from a specific domain (for example, alvosec.com).
DKIM: DomainKeys Identified Mail
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) authentication, on the other hand, makes sure that the content of the email is trusted and has not been compromised or tampered with during the delivery. Similar to SPF, the DKIM is added as a TXT record by adding it in the domain panel.
DMARC: Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance
Lastly, the Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance (DMARC) is also referred to as “email signing.” It ties the first two email security protocols (the SPF and DKIM) together with a more consistent set of policies.
In our spoofing test above we see that SPF failed, due to non-whitelisted server of amazon.com. Whenever you see that SPF failed you must be careful with the message.
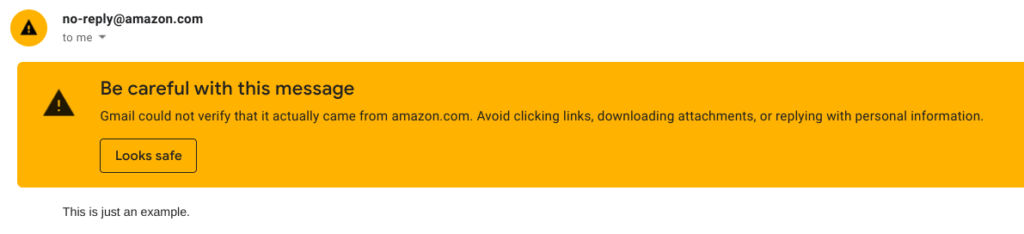
As it says in warning message, Gmail could not verify that it actually came from amazon.com.
Here is a second example of spoofing, where we didn't change an e-mail, but name of the sender which is under quotation marks. Some mail clients will show that as an actual sender, which may confuse users.
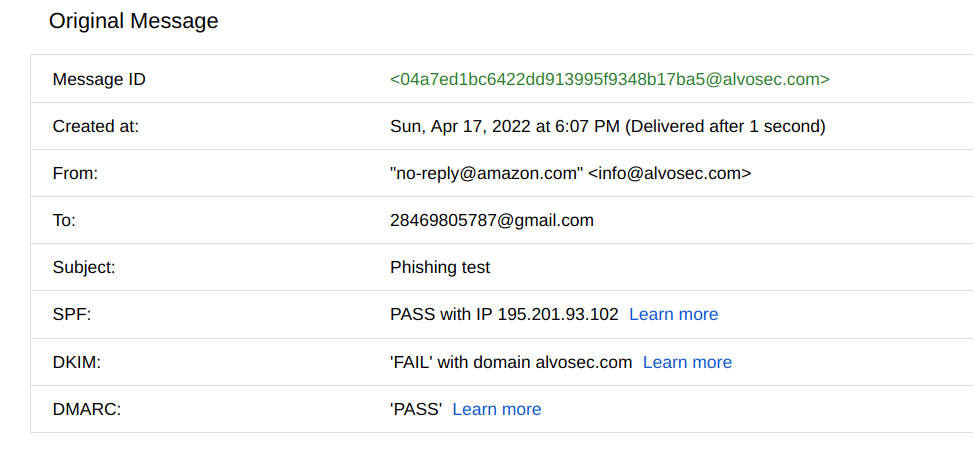
You can use this tool to analyze email headers.
Scammers are placing ads at the top of Google Search that imitate popular wallet brands, such as MetaMask or any other website, to trick users into giving up their wallet passphrase and private key.
When URL shorteners condense a link, the actual domain name of the site recipients will be directed to become obscured with random letters and numbers. There is nothing in those random figures to let the recipient know they’re clicking a malware link or being directed to a spoofing page where credentials can be stolen. While this would make some people hesitant to click, phishers knew the vast majority of people don’t know better, or can’t resist, so compromised shortened URLs began appearing in phishing emails and on social posts.
Attack of the clones: Beware of the fake social media accounts, where attackers are trying to clone either Telegram group, Facebook or Twitter page. You can read this article Investigation of websites and Telegram groups that are stealing private keys.
Here is an example of cloned Telegram groups pretending to be official support of Protonchain.
